Product Description
Product Description
|
OEM NO. |
49572 |
|
Car Fitment |
|
|
Place of Origin |
ZHangZhoug, China |
|
Material |
Aluminium |
|
Type |
Tensioner |
|
Size |
|
|
Reference NO. |
|
|
Truck Model |
|
|
Product Name |
Tensioner |
|
Packing |
Neutral Packing |
|
SHIPPING TERM |
Sea/Air |
|
Quality |
100%tested |
|
Size |
same as OEM |
Detailed Photos
Replacing a Failing Drive Belt Tensioner
A failing drive belt tensioner can be extremely costly. Here’s what to look for and what to do if you suspect yours is bad. In addition, you’ll learn how to identify Idler pulleys and repair it yourself. If the tensioner is failing, you should replace the belt, as well as the Idler pulleys and shaft bearings. But what if the tensioner isn’t faulty?
Symptoms of a bad or failing drive belt tensioner
If your car’s drive belt is not moving smoothly, the pulley may be at fault. Ideally, the tensioner pulley should move away from the engine when the car starts. However, if it stays put or starts to move toward the engine, it’s time to replace the tensioner. The belt may also start to exhibit different wear patterns, such as the uneven wear of the sprockets, bearings, and springs.
If the serpentine belt begins to look loose and the engine loses its luster, the problem is most likely the bad drive belt tensioner. This issue will result in engine vibration. A faulty drive belt tensioner may also lead to a faulty spark plug, which prevents fuel from burning in the combustion chamber. This issue will likely require an engine diagnostic tool, such as an OBD2 scanner, to determine the cause of the check engine light.
Another sign that your drive belt tensioner is failing is a chirping noise. This noise can occur intermittently or constantly, and it may signal a problem with the pulley. In some cases, a faulty pulley may even cause your engine to misfire. Additionally, you may notice that the engine won’t start, even if you engage the starter motor.
In addition to the noise that may come from a failing tensioner, the bad belt tensioner may cause your serpentine to fail. In addition to the noise, this can also lead to overheating of the engine, which can result in costly damages. In addition to causing engine damage, a bad belt tensioner won’t reserve the minimum tension it needs to do its job and may even exceed it, causing the belt to wear out much faster.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it may be time to replace the drive belt tensioner. You can find a replacement OEM part online at a discounted price, as they’re available in wholesale quantities. A Mazda engine typically has no other parts blocking the serpentine belt path, so you can easily find the part you need. After replacing the drive belt tensioner, you’ll need to replace the serpentine belt as well.
Cost to replace a drive belt tensioner
Depending on the location and type of vehicle, replacing a drive belt tensioner can cost between $235 and $267. Some repairs may require other parts, such as a serpentine belt or tensioner housing. RepairPal’s Fair Price Estimator can help you get an accurate estimate for your particular vehicle. You can also contact HomeX, a virtual repair shop that can fix simple issues like loose drive belt tension.
It’s a relatively simple DIY job for most cars. An experienced mechanic will be able to replace the belt in a half hour or less, depending on the type of car and how many parts are affected. Depending on the complexity of the repair, the labor to replace the drive belt tensioner could cost anywhere from $50 to $170. The labor to replace the drive belt tensioner is typically included in the quoted price, but some auto shops may charge more to replace other car parts as well.
Replacing the drive belt tensioner is a relatively easy task. While the process might take an hour or more, it will be worthwhile in the long run. Regular inspections can prevent costly repairs by identifying problems before they cause major damage. A car’s belt is essential to the operation of the engine and can’t be operated without it. Changing it can save you money, as it will save you from spending extra on unnecessary parts.
Thankfully, there are plenty of tools available to help you replace your drive belt. While it may not be the easiest repair, it will still cost less than a mechanic’s service call. It is better to replace the belt early than to wait for the vehicle to break down, as this will prevent more expensive parts from breaking. You may also consider investing in a premium belt, which will give you twice as much mileage as a cheaper one.
While a drive belt tensioner is generally considered a wear-and-tear item, it is a part that should last the entire life of the vehicle. You can expect to replace the drive belt tensioner no earlier than 125,000 miles, but it is better to do it early if your car isn’t that old. And it doesn’t hurt to check the owner’s manual for directions on how to replace the drive belt tensioner.
Idler pulleys
Idler pulleys may seem like a minor part of your car, but their important job is to keep various components in good working order. Fortunately, they are inexpensive and don’t need much maintenance. If 1 pulley fails, it is best to replace all of them. However, it is not always easy to check idler pulleys yourself. It’s recommended that you visit a professional auto repair shop that is ASE-certified to inspect and replace the idler pulley.
Depending on the size and type of idler pulleys you need, you’ll have to purchase 2 or 3 pieces. You’ll need to purchase a pair of pliers for this part, as well as a tensioner pulley wrench. The cost of a replacement idler pulley will vary by make and model, but you can expect to pay between $40 and $200. These prices don’t include taxes or fees. Because they are so essential to drive belts, it’s worth investing in 1 or two.
Idler pulleys are a vital part of a car’s engine. They’re found underneath the hood and are usually 2 to 4 inches in diameter. They run over a roller that’s used to tension the belt. The belt is wrapped around a series of engine parts, and the idler pulleys are a complement to each other. You may not need an idler pulley on your car, but your mechanic will install it for you if you don’t.
The idler pulleys for a belt tensioner are crucial parts of your car’s engine. If they are worn down, the belt is likely to move loosely over them. Corrosion may also make the idler pulley move less freely. If the idler pulley is slipping, the belt may jump over the pulley, and the squealing noises will indicate a serious problem.
The idler pulley is a pivotal part of the engine’s power train. It redirects the path of the serpentine and timing belts, so that they can make optimal contact. The larger the contact patch, the more power the belt will transfer. The idler pulley can also improve the vehicle’s performance. It is a vital part of the engine, so make sure you check it frequently and install it correctly.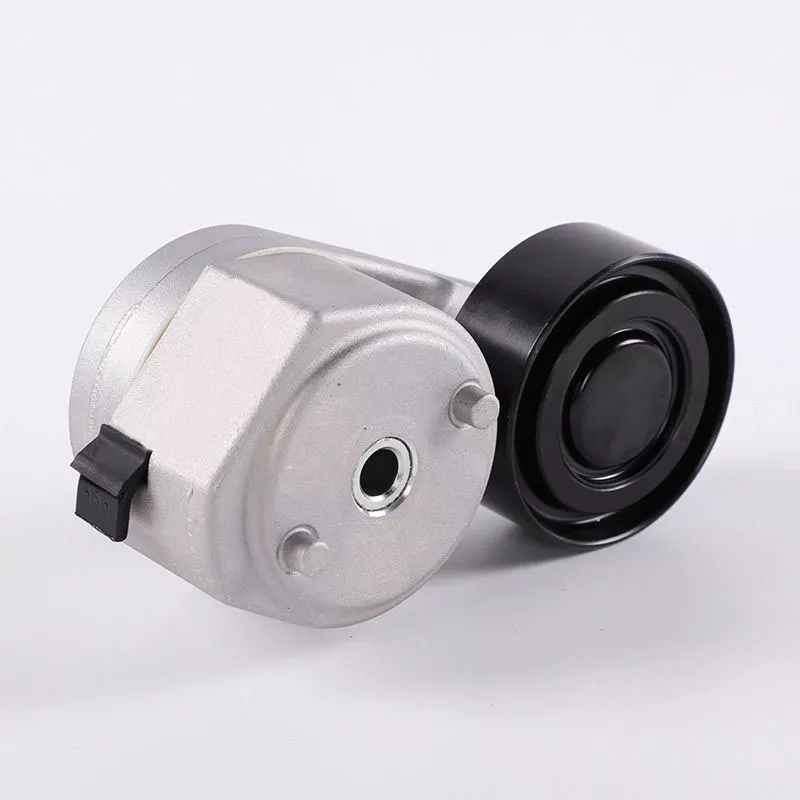
Repairing a drive belt tensioner
Replacing a drive belt tensioner is relatively simple. While your belt may need to be replaced, other parts of your engine may also need to be fixed. Typically, the tensioner will be replaced along with the pulley, as both parts are prone to malfunction. Replacing the drive belt tensioner is a fairly straightforward job, and it should only take about an hour or two. By following these simple steps, you can save yourself a lot of money and time.
You can detect the problem by observing the belt glazing. Typically, it occurs when the tensioner does not have enough spring tension. Another sign of a failed component bearing is excessive arm oscillation. Excessive chattering and oscillation indicate that the damper has worn out. If you notice excessive oscillation, you should replace the tensioner pulley. Otherwise, you might be dealing with a defective bearing.
A damaged or out-of-adjusted drive belt will make a squealing noise. This is due to the belt slipping on the pulleys. It is most noticeable when the car is first started in the morning. A damaged drive belt will also be hard to manipulate. The new belt should be the same length and width as the old one. You can check the tensioner by pulling the belt and compressing it.
A worn-out drive belt tensioner will result in unusual noise, excessive wear, and a loose belt. This is especially affecting if the car is equipped with a serpentine belt. The drive belt tensioner has a roller bearing that can wear out, which will cause a squealing noise or even cause the belt to roll off entirely. Because of its important role in engine operation, it is vital to check the condition of the drive belt tensioner on a regular basis.
While replacing a drive belt tensioner may seem like a simple DIY project, you should consult a mechanic before undertaking the work. The parts and labor costs of a drive belt tensioner repair can range from $140 to $400, and you should allow an hour for this repair. If you are not comfortable performing the repair yourself, you can always hire a mechanic to do it for you. In most cases, a drive belt tensioner replacement will cost approximately $70 to $80 and take about an hour.